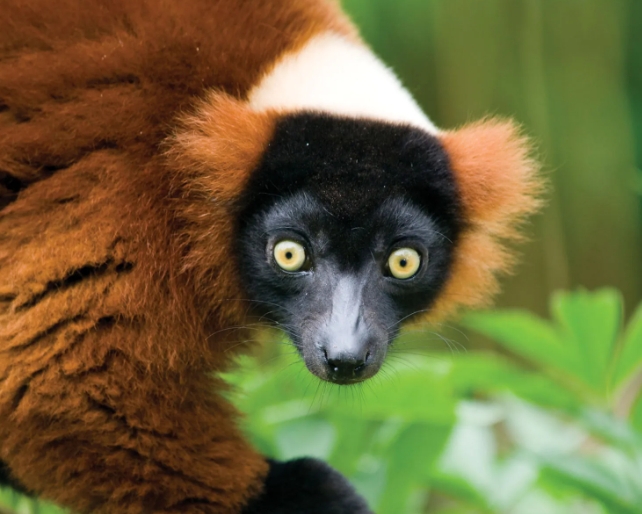
Lemurs are fascinating creatures native to the island of Madagascar, completely endemic to this unique ecosystem.
Madagascar is home to over 100 species of lemurs, ranging in size from the tiny mouse lemur to the larger indri lemur.
These primates have evolved in isolation, developing a remarkable diversity of physical characteristics and behaviors.
Lemurs are known for their large, expressive eyes, which help them see clearly in the dense forests where they live.
They have a keen sense of smell, using their long, sensitive noses to locate food and communicate with one another.
Types of Lemurs
There are many different types of lemurs, each with its own unique characteristics. Some of the most well-known species include the ring-tailed lemur, the black-and-white ruffed lemur, and the sifaka lemur.
Ring-tailed lemurs are perhaps the most iconic of all lemurs, with their distinctive ringed tails and social behavior. They are known for their complex vocalizations and the way they huddle together for warmth.
Black-and-white ruffed lemurs, on the other hand, are known for their striking black-and-white coloration and their acrobatic leaping abilities. They are also one of the most endangered species of lemurs, making them a priority for conservation efforts.
Sifaka lemurs are known for their unique way of moving – they leap through the trees by pushing off with their powerful hind legs, giving them a distinctive, almost dance-like appearance.
Conservation Challenges
Lemurs are facing numerous threats in the wild, including habitat loss, hunting, and the illegal pet trade.
Deforestation is a major issue in Madagascar, with large swathes of forest being destroyed to make way for agriculture and development. This destruction not only threatens the lemurs themselves, but also the countless other plant and animal species that call Madagascar home.
Hunting is another major threat to lemurs, with some species being targeted for bushmeat or for their fur. This, combined with the fact that many lemurs are slow to reproduce and have small population sizes, puts them at risk of extinction.
The illegal pet trade is also a problem, with lemurs being taken from the wild and sold as exotic pets. This not only harms wild populations, but also leads to the mistreatment and neglect of these highly social animals.
Conservation Efforts
Despite these challenges, there are many dedicated individuals and organizations working to protect lemurs and their habitats.
Conservation groups are working to establish protected areas and wildlife corridors in Madagascar to help safeguard lemurs and other wildlife.
Education and outreach programs are also key in raising awareness about the importance of lemurs and the need to protect them.
By supporting these efforts and learning more about lemurs and their unique place in Madagascar’s ecosystem, we can all play a role in ensuring the survival of these iconic primates.