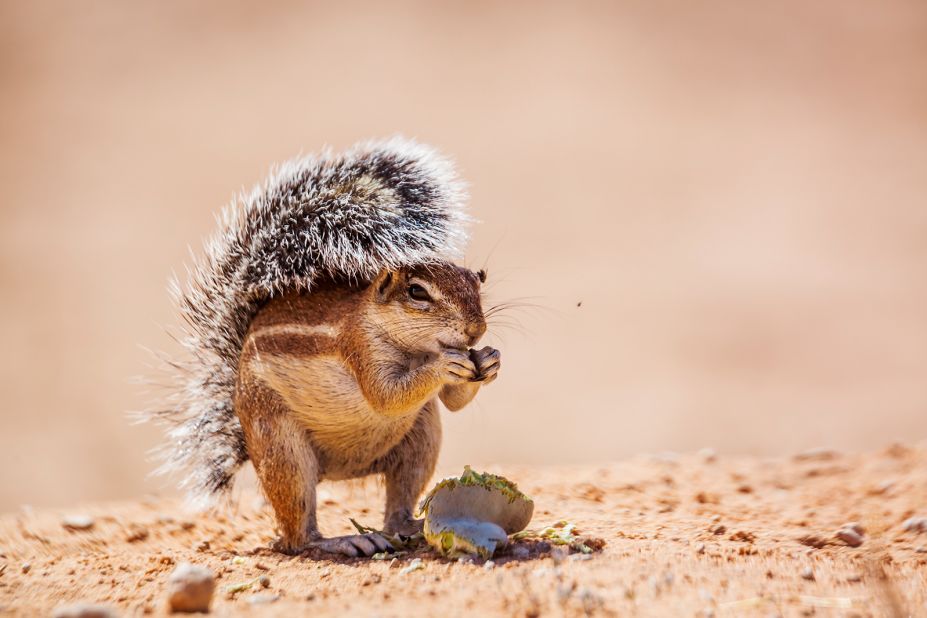
How do Ground squirrels survive in extreme heat? Ground squirrels inhabit regions where temperatures can soar to extreme levels, presenting a formidable challenge for their survival. Despite these harsh conditions, ground squirrels have evolved remarkable adaptations that enable them to thrive in hot environments. Let’s explore the ingenious strategies employed by these resilient creatures to beat the heat and flourish in their arid habitats.
Burrowing Behavior: Seeking Shelter Underground
When temperatures rise to scorching levels, ground squirrels retreat to the safety of their underground burrows. These burrows provide a cool refuge from the blazing sun, shielding the squirrels from the oppressive heat above ground. By digging deep into the earth, ground squirrels create a network of tunnels that not only offer protection from high temperatures but also serve as shelter from predators.
Estivation: A Survival Strategy for Hot Summers
During the hottest months of the year, ground squirrels may enter a state of dormancy known as estivation. Similar to hibernation, estivation allows these animals to conserve energy and water during periods of extreme heat and drought. By lowering their metabolic rate and remaining inactive in their burrows for extended periods, ground squirrels can survive harsh environmental conditions without depleting their energy reserves.
Cooling Mechanisms: Behavioral Adaptations
Ground squirrels employ various behavioral adaptations to stay cool in hot weather. One such adaptation is spreading their bodies flat against the ground to maximize contact with cooler surfaces. Additionally, they may seek out shaded areas or moist environments, such as the banks of streams or ponds, to escape the heat. Some species of ground squirrels also engage in communal cooling behaviors, gathering together in shaded areas or sharing burrows to reduce individual heat stress.

Physiological Adaptations: Coping with Heat Stress
To cope with extreme heat, ground squirrels have evolved physiological adaptations that enable them to regulate their body temperature more effectively. These adaptations may include increased water conservation mechanisms, such as concentrating urine to minimize water loss, and modifications to their circulatory system to facilitate heat exchange. By efficiently managing their internal temperature, ground squirrels can withstand prolonged exposure to high heat without suffering heat-related illnesses.
Foraging Strategies: Navigating Scarcity in Arid Environments
In arid environments where food and water are scarce, ground squirrels have developed specialized foraging strategies to survive. They may rely on opportunistic feeding behaviors, consuming a diverse array of plant materials, seeds, and insects to meet their nutritional needs. Additionally, ground squirrels are known for their caching behavior, storing food in underground chambers within their burrows to sustain them during periods of scarcity. By adapting their foraging habits to their environment, ground squirrels can thrive in regions with limited resources.
Conclusion: Masters of Survival in the Desert Landscape
How do Ground squirrels survive in extreme heat? Despite the challenges posed by extreme heat, ground squirrels have evolved an impressive array of adaptations that enable them to thrive in their arid habitats. From seeking shelter underground to entering states of dormancy, these resilient creatures have mastered the art of survival in the desert landscape. By understanding the strategies employed by ground squirrels to cope with high temperatures, we gain insight into the remarkable resilience of wildlife in the face of environmental adversity.